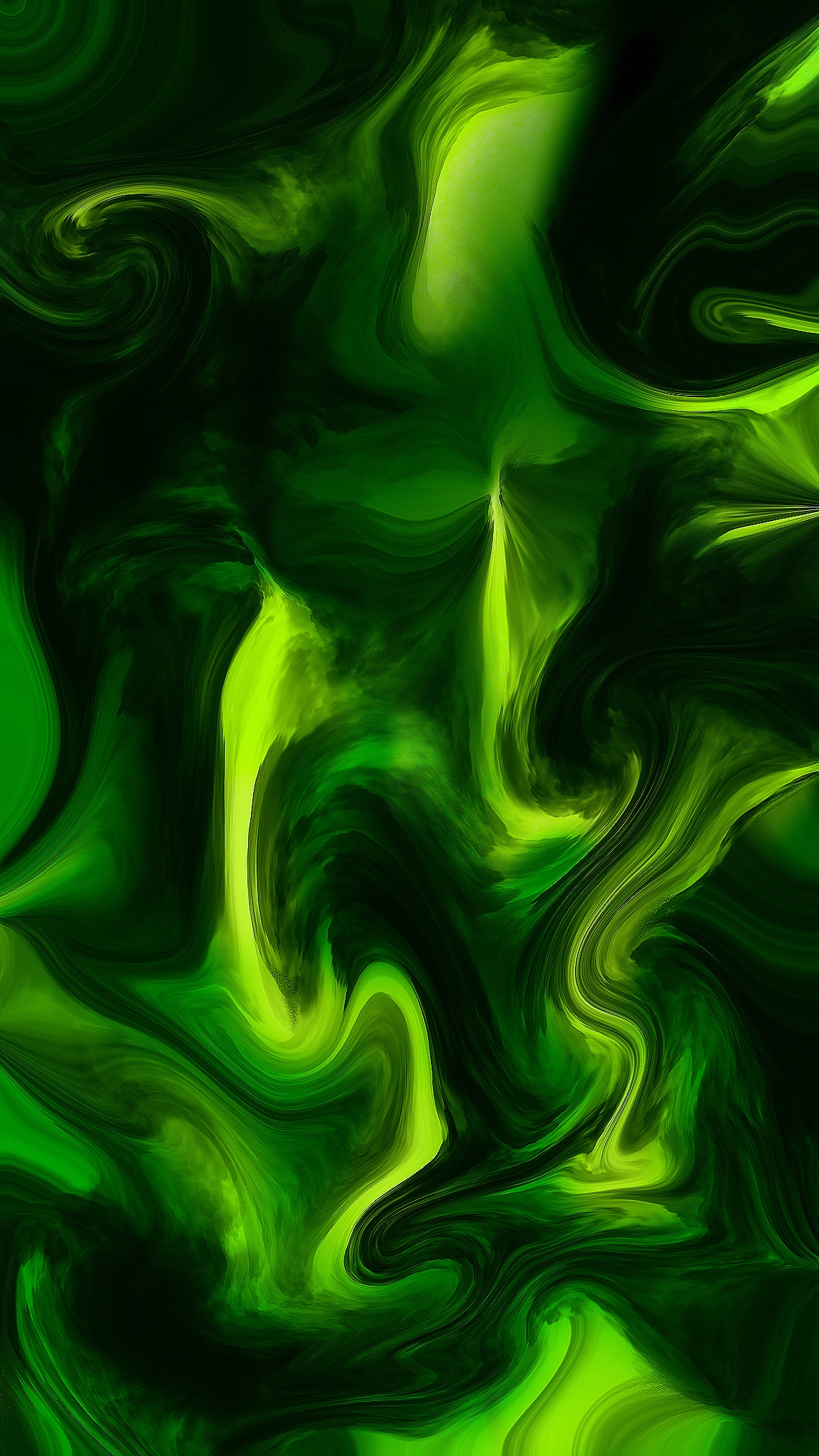

Pressure
Pressure is the amount of force exerted per area.
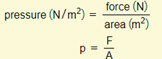
As the temperature increases, pressure increases as the molecules strike the wall of the container more frequently and this gives a GREATER CHANGE IN MOMENTUM. As the change in momentum increases per second, the force exerted increases and therefore provides a greater pressure for a constant surface area.
Measuring pressure
1)Mercury barometer
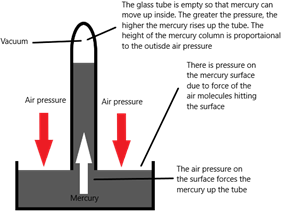
The pressure at beneath a liquid surface (and therefore at the base of the mercury column) can be calculated with the following formula:
Pressure beneath liquid surface = ρgh
[ρ = density (kg/m3), g = acceleration due to gravity (10 m/s2), h = depth (m)]
2) Manometer
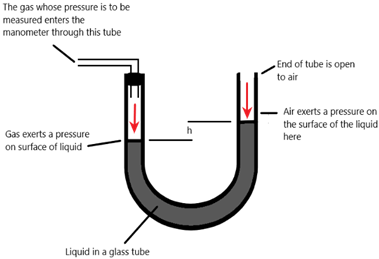
Pressure due to gas = atm + ρgh
[ρ = density (kg/m3), g = acceleration due to gravity (10 m/s2), h = depth (m)]
[atm = atmospheric pressure]
