
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Summary of electromagnetic spectrum
All electromagnetic waves can travel through vacuum. They all travel at the speed of 3 X 10^8 m/s in vacuum and very close to this value through air.
In other materials however, they travel a bit slower. Each selection of the electromagnetic spectrum has its own uses and features:
| Region | Frequency Range (Hz) | Wavelength Range (M) | Applications |
| Radio | 105 – 1010 | 104 – 10-2 | Electromagnetic oscillations produced by electric circuits; Received by aerial and used in communication |
| Microwave | 1010 – 1011 | 10-2 – 10-3 | Used for rapid heating in microwave; Used to communicate with satellites i.e. mobile phones |
| Infra-red | 1011 – 1014 | 10-3 – 10-6 | All hot objects produce infrared; Used for night goggles, burglar alarms, etc. (since all humans emit infra-red) |
| Visible | 1014 | 10-7 | Produced by very hot objects such as the sun; Detected by the eye; Used in optical fibres communication |
| Ultraviolet | 1015 -1017 | 10-7 – 10-9 | Causes fluorescence in some materials; Uses with sunbeds to produce sun tan |
| X-Radiation | 1017 – 1019 | 10-9 – 10-11 | Blackens photographic film; Used in diagnosis (X-Ray scan); Dangerous in high doses |
| Gamma Radiation | 1019 – 1020 | 10-11 – 10-14 | Produced in nuclei of radioactive elements; Used in medical diagnosis but dangerous in high dosage |
The higher the frequency, the higher the energy of the radiation. Therefore, radio waves have the lowest energy and gamma radiation has the highest energy within the spectrum.
COMMUNICATIONS USING THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM:
Some satellite phones use low orbit artificial satellites.
Geostationary satellites orbit above the earth’s equator and are used in satellite phones and direct broadcast satellite tv around the world due to its high orbit.
POLAR SATELLITES:
These are Low orbit satellites and orbit around Earths North and south poles
They are used for monitoring weather and taking images of the earth’s surface.
Time delay is shorter, and signals and images are clearer BUT have limited use in one orbit as more than one satellite is required for continuous operation.
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS:
Radio waves: transmit signals over short distances and we can receive these signals in hilly areas as radiowaves can diffract.
BLUETOOTH uses radio waves as radio waves pass through walls, but the signal becomes drastically weakened.
MICROWAVES:
Transmit signals over large distances. Used to send signals between satellites and stations and are also used in phones and weather forecasting
Phones and Wi-Fi use microwaves because microwaves penetrate some walls and only require a short aerial for transmission and reception.
OPTICAL FIBRES:
Used for high-speed broadband and cable tv, as transparent glass allows for efficient total internal reflection of visible and infrared light to occur and these two can carry high rates of data due to the relatively high frequencies of the waves.
Sound can be transmitted as a digital or an analogue signal.
SIGNALS:
Digital- take the form of one or two discrete states, 0 or 1
Analogue- continuously varying and can take any value
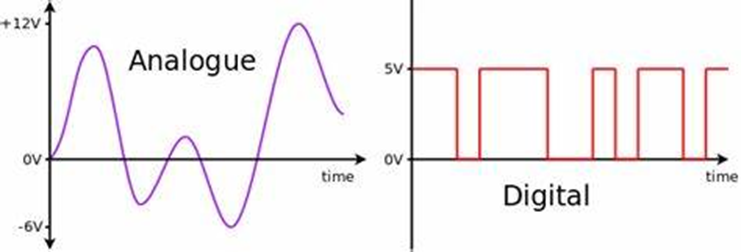
ADVANTAGES OF DIGITAL SIGNALS- signals are clearer and carry more information. Transmission of data is faster and the signals have a large range due to accurate signal regeneration. DISADVANTAGES: Very expensive and don’t give a complete signal
