Opportunities, risks, legal and ethical decisions
Changing Needs and Wants for Products:
Understanding how customer needs and wants evolve is crucial for business success. Here are some key factors driving change in product needs and wants for IGCSE Business students:
1. Technological Advancements:
- New technologies constantly emerge, creating new possibilities and expectations for products.
- Examples include:
- Increased demand for smart devices and internet connectivity in everyday products.
- Growing preference for mobile apps for shopping, banking, and communication.
- Expectation of faster processing speeds, larger storage capacities, and improved user interfaces.
- Reduction in demand for products such as CRTs and DVDs
2. Shifting Demographics:
- Changes in population demographics can significantly impact product needs and wants.
- Examples include:
- The growing aging population might require products designed for accessibility and senior living.
- The rise of dual-income households could lead to demand for time-saving appliances and convenience foods.
- Increasing urbanization may influence demand for space-saving furniture and compact living solutions.
3. Social and Environmental Concerns:
- Consumers are becoming more conscious of social and environmental issues.
- This can lead to a demand for:
- Products made with sustainable materials and ethical production practices.
- Eco-friendly packaging and reduced environmental impact.
- Products that promote healthy lifestyles and well-being.
4. Economic and Governmental Factors:
- Economic conditions can influence purchasing decisions and product preferences.
- During economic downturns:
- Consumers might prioritize affordability and value for money.
- Increased demand for budget-friendly alternatives and multi-functional products.
- During economic booms:
- Consumers might be more willing to spend on premium products and innovative features.
- Changes due to the government:
- Availability of grants and subsidies can boost or kill some enterprises. They may allow startups to survive, under performing sectors to be boosted, etc.
- Changes in taxes can help companies and may also allow people spend more with reduced personal taxes
- Changes in law make it easier for new products to be made, make it easier for businesses to be setup, etc.
5. Evolving Trends and Fashions:
- Consumer preferences regarding style, design, and functionality change over time.
- Businesses need to adapt to:
- Trending colors, patterns, and aesthetics.
- Changing fashion trends in clothing, accessories, and homeware.
- Evolving consumer preferences for product features and functionalities.
Remember:
- Staying informed about these factors and conducting market research is crucial for businesses to adapt and create products that meet evolving customer needs and wants.
- Businesses that anticipate and respond to changing trends can gain a competitive advantage.
Risks involved in enterprise
Starting and running an enterprise involves inherent risks. Here are key areas of risk to consider:
1. Financial Risk:
- This refers to the possibility of financial loss for the enterprise. Examples include:
- Insufficient funds: Not having enough capital to start, operate, or grow the business.
- Poor cash flow: Difficulty managing cash inflows and outflows, leading to cash shortages.
- Debt burden: Difficulty repaying loans or incurring high-interest rates, impacting profitability.
- Unexpected expenses: Unforeseen costs like equipment failures, legal issues, or market fluctuations.
2. Economic Risk:
- This refers to external economic factors impacting the enterprise’s performance. Examples include:
- Economic downturns: Reduced consumer spending due to recessions or economic crises.
- Incorrect estimation of customers and customer taste due to improper market research
- Inflation: Rising costs of raw materials, labor, and production, affecting profit margins.
- Interest rate changes: Fluctuations in interest rates impacting loan repayments and borrowing costs.
- Currency fluctuations: Changes in exchange rates affecting import/export costs and international sales.
3. Health and Safety Risk:
- This refers to the potential for accidents, injuries, or illnesses related to the enterprise’s operations. Examples include:
- Workplace accidents: Injuries to employees due to unsafe work environments or improper equipment.
- Product liability: Products causing harm to customers, leading to lawsuits and compensation claims.
- Safety regulations: Failure to comply with health and safety regulations resulting in fines or business closure.
- Environmental hazards: Pollution caused by business activities leading to environmental damage and fines.
4. Human Resource Risk:
- This refers to issues related to the people employed by the enterprise. Examples include:
- Recruitment and retention difficulties: Finding and keeping qualified employees can be challenging.
- Employee turnover: High employee turnover can lead to lost productivity and increased training costs.
- Low employee morale: Unmotivated or dissatisfied employees can impact productivity and customer service.
- Skills gap: Employees may lack the necessary skills or training to perform their jobs effectively.
Remember for:
- Identifying and mitigating risks is crucial for enterprise success. Different strategies can be implemented for each risk type, such as financial planning, economic forecasting, safety protocols, and effective HR practices.
- By understanding these risks and taking proactive measures, entrepreneurs can minimize their impact and ensure the smooth operation of their business.
The stages of risk management:
- Stage 1: Identify the risks
- Stage 2: Analyze the implications of each risk
- Stage 3: Is the risk worth taking – (if not worth, then stop the project)
- Stage 4: If worth taking the risk, then how to manage the risk
- Stage 5: Monitor & review
Stage 1: Identify the risks –
Identify various risks possible to the entrepreneurship using methods of risk analysis such as SWOT, PEST.
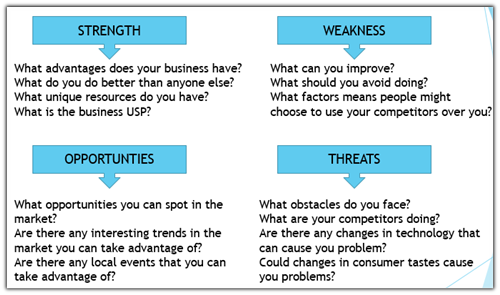
Stage 2: Analyze the implications of each risk –
For each risk identified, consider the following;
- What are the chances of it happening?
- What are the potential consequences?
- Analyze the positive & negative effects
- Assess the potential negative effects against the potential rewards
- If possible rewards outweigh the negative risks, then proceed with the project.
Stage 3: Is the risk worth it? –
- This depends on the entrepreneurs attitude towards risk
- If he is risk averse, he may discontinue or if he is a risk taker he will proceed with the project.
Stage 4: Plan to manage the risk –
- Mitigate: try reducing the risk by changing the risk
- Accept: If nothing can be done about the risk, then set aside a sum to cover up any negative effects of risk
- Transfer: Pass on the risk to an outside agency who will be able to better manage the risk
- Eliminate: If you chose to avoid risk, you will have to give up on the positive impact of the risk.
Stage 5: Monitor and Review
Reducing Risk –
- Detailed research- PEST/ SWOT analysis
- Seek advice from formal / informal support
- Prepare a business plan
- Spread the risk through diversification. It is the process of selling products or selling to different markets.
Monitoring Risk –
Risks can change over time. Changes can happened due to internal and external factors that keep changing. Therefore risks have to be constantly monitored.
Attitudes to Risk –
- One can be risk averse, which means he avoids risk most of the times, or all of the time.
- He can also choose to be risk keen, or always ready to take risks as he might believe that’s the only way to grow his business.
- They can also be risk reducers, who take risks, but mitigate it enough to not harm their business if anything goes sideways.
Legal obligations –
- Employment- Contracts to be made to resolve disagreements. Minimum wage laws should be followed.
- Production, health & safety laws
- Laws relating to marketing and selling to protect customers
- Finance: laws regarding money invested to protect interest of shareholders.
Ethical Considerations –
- Ethics: Moral values and principles that govern a person’s behavior or the conducting of an activity.
- Being ethical involves actions and behavior that go beyond what is legally required
- Ethics and profit can conflict.
- An ethical firm considers the impact of its decisions on all the stakeholders
Advantages of being ethical –
- An ethical brand image can lead to better reputation
- Can attract customers
- Can attract new employees and help retain the existing ones.
- Suppliers will be willing to supply goods and offer discounts
- Lenders may be willing to offer support
- Can provide a USP (unique selling point)
Disadvantages of being ethical –
- Increased cost of purchasing materials
- Expectations from the employees, customers, suppliers, etc.
- Additional cost involved
