Introduction to Enterprise
Enterprise is another word for organization or business managed by one or more individuals who are able to take the initiative to make decisions and take calculated risks.
Types of Enterprise
- Business Enterprise (Trading Business) – A business enterprise is an organization that has profit as its main aim.
- Service/Social Enterprise (Service Business) – It is an organization that is started for social cause or for the betterment of the society
Who is an Entrepreneur?
A person who takes the initiative to set up a business, make decisions and takes on financial risks in the hope of making profit.
Key Attributes that comprise enterprise capability –
- Risk Taking
- Creativity
- Leadership and more…
Risk Taking –
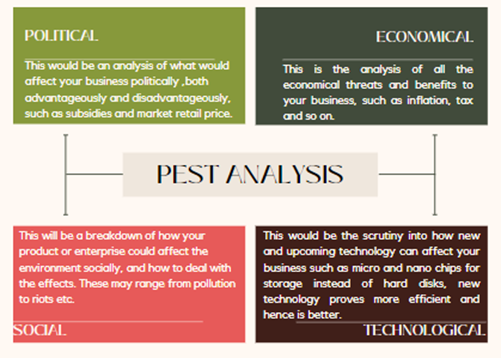
Risks are a major factor in ensuring a successful business because without the ability and confidence to take risks when needed to, the business wouldn’t prosper. That doesn’t take away the fact that one must be careful when taking risks because decisions have to be evaluated with caution before being executed. There are a number of ways we could evaluate and analyze, one of which is PEST Analysis.
Creativity –
This is a major skill that is needed in all entrepreneurs and it assists them in building a successful enterprise. Without a product or an individuality that separates your product or enterprise from others, profit would not be the outcome, nor would success be one. The goal is to fulfill the gap in the market, and bring something new, this can involve latest trends and fashions, twists in a generic product, adding a technological aspect and so on.
Leadership –
Leadership is an attribute that is necessary in all types of businesses. A leader shares a vision and direction with his employees so they all have a shared goal. They don’t leave them stranded, however, doesn’t also do all the work himself, instead, he supports and teaches important skills in workplaces, and brings the fire in them to work hard. This will provide for a better work environment, and improve quality and productivity. It can be a turning point in any company’s success.
Who are Stakeholders?
A stakeholder is an individual, group or organization with an interest in the activities of a business and usually there are two types:
Types of Stakeholders –
| Internal Stakeholders | External Stakeholders |
| Employees | Customers |
| Owners | Government |
| Shareholders | Local Community |
| Managers | Suppliers |
Stakeholders
- Stakeholders are people, groups, or organizations that have an interest in an enterprise. They can be affected by the enterprise’s actions, objectives, and policies, and vice versa.
- Some examples of key stakeholders in an enterprise are customers, consumers, employees, employers, suppliers, lenders, the local business community, and local government.
Customers
- Customers are very important to the survival and success of an enterprise. They buy the goods and services that are supplied by enterprises. It is important for enterprises to understand the needs and wants of their customers.
Employees
- Employees are employed by an enterprise to help its activity in some way. An enterprise needs employees with a range of skills and knowledge and many will provide training to new employees to familiarize them with the policies and working practices of the enterprise.
Suppliers
- Suppliers
- Businesses that provide resources to other businesses for producing goods and services.
- Examples of resources include raw materials, component parts, tools, equipment, energy, and various services.
- Both businesses and suppliers rely on each other, so a good working relationship is important.
- Key requirements for businesses from suppliers
- High-quality resources at reasonable prices
- Reliable and flexible service
- Key requirements for suppliers from businesses
- Consistent flow of orders
- Timely payments
Lenders
- Lenders
- Financial institutions that businesses can borrow money from to operate or grow.
- A good relationship is necessary between the borrowing business (borrower) and the lender.
- Key requirements for businesses from lenders
- Access to loans when needed
- Key requirements for lenders from businesses
- Repayment of the loan plus interest
Local business community
- Enterprise will usually employ workers from around them. The more the enterprise hires locally, the better the chances that ther eis a good relationship between the company and the local people. For example, enterprises can get help from unis for training and research and companies can also sponsor local events, etc.
Local government
- Companies may have to work with the different local and national governments, for example for work permits, taxes.
