eSafety, and health and safety
Security of data
There are various different methods on how data is frequently collect for unauthorized purposes these are the common methods that are used and how one can prevent such acts from occurring
Smishing
- Short for SMS phishing.
- Similar to phishing but is carries out via SMS text messaging rather than email.
- It is carried out when an SMS text message is sent to a user that will ask them to telephone a number or click on a link. When that number is telephoned, the person receiving the call will attempt to get the personal details of the caller.
There are measures that can be taken to protect against smishing
- Users should be very cautious in telephoning any numbers they are sent in an SMS message
- Users should be very cautious when clicking on any links in messages.
- Users should not install any applications from senders they do not know.
- If a user receives a suspicious message from someone they do know, they should check with the person that they have actually sent that message.
- Users should be wary of numbers that do not look like usual mobile numbers, such as ‘5000’.
- Users can add security software to their mobile to help detect any malware
Vishing
- Short for voice phishing
- It is usually done when the caller tries to scam the user into revealing g their personal data. The scammer will usually pretend they are from a legitimate business calling the person.
- The person vishing will either say that they are alerting the victim to an issue with their account, or advising the victim of a profitable gain
- Often elderly and vulnerable are considered victims
There are measures that can be taken to protect against vishing:
- People should exercise caution when any institution contacts them, especially when they ask for personal details. If in doubt hang up and call them back on a number that is known.
- People should never give out any personal details regarding a security issue with their account. A bank will prevent any kind of attack on an account without needing assistance from the account holder.
Phishing
- Phishing is when an unauthorized person attempts to gather personal data, such as passwords and credit card details, by disguising themselves as a trustworthy person or organization
- Phishing is normally carried out via electronic communication, such as email. The email will look legitimate and will normally encourage a person to click on a link in the email. When the link is clicked it will take the user to a website that will ask them for their personal details.
- Phishing emails will usually contain text that will express the need for urgent attention to a matter.
There are measures that can be taken to protect against phishing:
- Users should make sure that they are cautious when clicking any links in an email.
- Users should question whether they know the sender of the email and only open links from known senders.
- Users should check the URL that they are being linked to, to see if itis legitimate. This can be done by hovering over the link and looking to see if the address is the real address of the site, for example www.paypal.com would be legitimate but www.paipal.com would be identified as fake because of the spelling mistake.
- Another thing that should raise suspicion is any spelling or grammatical errors in the email content
Pharming
- Pharming is another method of collecting personal data.
- A hacker will install malicious code onto a person’s computer or server. When a user types in a web address they will be redirected to a fraudulent, but legitimate looking, replica website, without their consent.
- The user will continue using the website as they normally would, unaware of the redirection, and enter their personal details that will then be stolen.
There are measures that can be taken to protect against pharming:
- Users should check if the website looks the same as when they last visited it.
- Users should look for the padlock security symbol used to signify the HTTPS, showing that the website is secure, before entering any personal and financial details.
- Users should run regular scans of their computer with anti-virus software that is designed to detect pharming programs.
Malwares issues
Malware is a computer program that is designed to damage or disrupt a computer system and the files that are stored on it.
Malware can take many forms here is list of few of them.
Trojan Horse
Trojans are a class of malware that take their name from the way they infect computers. Trojans hide themselves within seemingly harmless programs or try to trick you into installing them.
Trojans do not replicate by infecting other files or computers. Instead, Trojans survive by going unnoticed: they may sit quietly in your computer, collecting information or setting up holes in your security, or they may just take over your computer and lock you out.
Some of the more common actions that Trojans take are:
Creating backdoors: some Trojans will make changes to your security system so that your data and device can be accessed by their controller.
Spying: some Trojans are designed to wait until you access your online accounts or enter your credit card details, and then send your data back to whoever is in control.
Steal you passwords: some Trojans are made to steal your passwords for your most important online accounts.
Worms
Computer worms are similar to viruses in that they replicate functional copies of themselves and can cause the same type of damage. In contrast to viruses, which require the spreading of an infected host file, worms are standalone software and do not require a host program or human help to propagate. To spread, worms either exploit a vulnerability on the target system or use some kind of social engineering to trick users into executing them. A worm enters a computer through a vulnerability in the system and takes advantage of file‐transport or information‐transport features on the system, allowing it to travel unaided.
Malicious Bots
“Bot” is derived from the word “robot” and is an automated process that interacts with other network services. Bots often automate tasks and provide information or services that would otherwise be conducted by a human being. A typical use of bots is to gather information (such as web crawlers), or interact automatically with instant messaging (IM), Internet Relay Chat (IRC), or other web interfaces. They may also be used to interact dynamically with websites.
Bots can be used for either good or malicious intent. A malicious bot is self‐propagating malware designed to infect a host and connect back to a central server or servers. In addition to the worm‐like ability to self‐propagate, bots can include the ability to log keystrokes, gather passwords, capture and analyze packets, gather financial information etc.
Adware
Adware software can display and/or download advertisements and may be considered privacy‐invasive. Adware tracks your computer’s web usage to feed you undesired ad pop ups or redirect you to unwanted pages.
Adware can hijack your home page and take you to sites you aren’t interested in, allow pop up ads that are disruptive to your system. Since they run every time you turn on your computer, they can cause slowdowns and software conflicts that can make your computer unstable.
Rootkit
Rootkit is an application (or set of applications), that hides its presence or presence of another application (virus, spyware, etc.) on the computer, using some of the lower layers of the operating system, which makes them almost undetectable by common anti‐malware software.
Rootkit can get to a computer using various ways. The most common way is through some trojan horse or some suspicious email attachment. Also surfing the web may result in installation of a rootkit, for example when “special” plugin (pretending to be legitimate) is needed to correctly view some webpage, to launch some file, etc.
Ransomware
Ransomware stops you from using your PC. It holds your PC or files for ransom. There are different types of ransomware. However, all of them will prevent you from using your PC normally, and they will all ask you to do something before you can use your PC.
They can:
Prevent you from accessing Windows.
Encrypt files so you can’t use them.
Stop certain apps from running (like your web browser).
Often the ransomware will claim you have done something illegal with your PC, and that you are being fined by a police force or government agency.
These claims are false. It is a scare tactic designed to make you pay the money without telling anyone who might be able to restore your PC.
There is no guarantee that paying the fine or doing what the ransomware tells you will give access to your PC or files again.
How malware can be avoided ?
Malware can be very difficult to remove from a computer system. It can often take numerous scans from anti-virus software, as well as the use of various malware removal programs, depending on the type of malware infecting the system.
There are number of measures that can be taken to avoid malware
A user should never open a program unless they know it is legitimate.
A user should have a firewall in place that is monitoring their internet traffic.
A user should regularly run an anti-virus check and malware detection software on their computer system, to detect the presence of any malware. Any anti-virus or malware detection program should be kept up to date in order to detect newly developed malware.
A user should not open any attachments to emails from unknown users.
A user should use open Wi-Fi points with extreme caution as anybody could be connected to them.
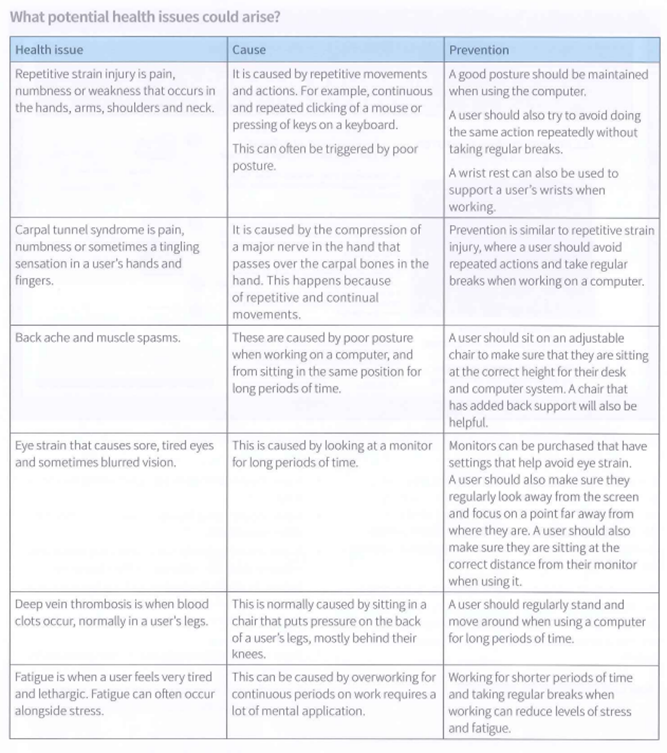
Health and safety