Market Failure
Market
Where buyers and sellers trade in goods and services
Wants
A want is simply something a person would like to have
Needs
A need is something that is necessary for survival (such as food and shelter)
Scarcity
The fact that there is a limited amount of resources to satisfy unlimited wants
Choice
It is a decision about alternative uses of scarce resources in the market
Market mechanism
Where decisions on price and quantity are made on the basis of demand and supply alone
Opportunity costs
It is the next best alternative for any product
Factors of production
Land: It is a natural resource that includes lakes, rivers, forests and mineral deposits
Labour: The people able to transform resources into goods or services available for purchase
Capital: A company’s physical equipment and the money it uses to buy resources
Enterprise : It combines all the three factors, to carry out the production process
Production and consumption
Production : The process of creating goods and services in an economy
Consumption: The process by which consumers satisfy their wants
Ceteris paribus: It is a Latin term used by economists, which means “other things remain equal”
Short run: it is a time period when a company can only change some and not all factor inputs (This is a time period of fewer than four-six months
Long run: Time period when all factors of production are variable ( A time period of greater than four to six months/ one year ) . eg: A firm can build a better factory
Very long run: Time period where all factors of production are variable and additional factors outside the control of the firm can change, eg: Government policies and technology
Positive and Normative statements
Positive statement : It is based on empirical values
Normative statement : It is a subjective statement of opinion which cannot be tested.
Division of Labour
It is a process where a manufacturing process is split into individual tasks
Advantages
- Increased productivity(higher output per worker per hour)
- Higher living standards
- Increased productivity leads to reduced cost per unit of output and therefore increases efficiency.
- Worker becomes highly skilled in a particular task due to repitition
- No time is wasted moving from one job to another
- Less time required to train workers for specific tasks
- More choice as workers can specialise in jobs they are most suited to
Disadvantages
- Boredom from repetition
- Division of labour creates interdependence in production. If one group of workers goes on strikes it brings the whole production process to a holt.
Resource Allocation
Economic structure : The way in which an economy is organized in terms of sectors
Primary sector : Consists of agriculture, fishing and activities such as mining and oil extraction
Secondary sector: Manufacturing activities found in an economy such as iron and steel production, electronics and textiles
Tertiary sector : Consists of service sectors like banking, education, retailing
Quaternary sector : They are the knowledge-based part of the economy. Eg: Scientific research and product development, computing and ICT
Economic system
They are the choices that are made in an economy
There are 3 types of an economic system- market economy, planned/command economy and mixed economy
Market Economy
A market economy functions under the laws of supply and demand. It is characterized by private ownership, freedom of choice, self-interest, optimized buying and selling platforms, competition, and limited government intervention. Competition drives the market economy as it optimizes efficiency and innovation.
Advantages
- Efficient
- Government freedom
- Quick response
- Consumer Sovereignty
Disadvantages
- Merit goods could be under consumed
- Demerit goods could be over consumed
- Advertising distortion
Planned Economy
In a centrally planned economy, major economic decisions are made by a central authority. Under a planned economy, unemployment is not an issue. The government are responsible for the allocation of resources, the determination of production targets for all sectors of the economy, the ownership of most productive resources and property and planning the long term growth of the economy
Advantages
- Merit goods are encouraged
- Employment levels increase
- Less waste of products due to proper planning
- Demerit goods are discouraged
Disadvantages
- Lack of consumer sovereignty
- Less competition
- Unresponsive
Mixed Economy
It involves both private and public sectors in the process of resource allocation. Mixed economies typically maintain private ownership and control most of the means of production, but often under government regulation .
Advantages
- Freedom of choice
- It encourages private initiative
- Less income inequality
Disadvantages
- Exploitation of labour
- There is more emphasis on profit at the expense of the welfare of the citizens
- There is usually high levels of corruption and mismanagement
Transitional Economy
It is the process where the government changes from planned to mixed economy
Problems in transitional economy
- Unemployment
- Industrial unrest due to change in lifestyle
- Fall in output
Production possibility curve
It joins together the different combinations of products that can be produced in an economy. It is used to show the tradeoffs associated with allocating resources between the production of two goods
Causes of PPC shifting to the right
- An increase in resources
- Increase in labor supply
- More capital and better resources are used
Causes of PPC shifting to the left
- Decrease in resources
- Unemployment
- Fall in capital
There are two types of ppc graph
- Straight line graph
- Curved line graph
Straight line PPC graph
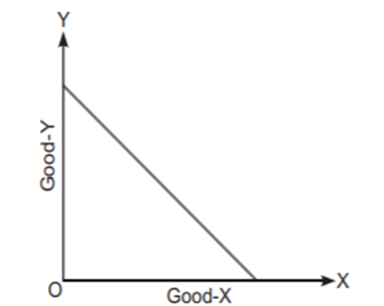
In a straight line PPC graph, the opportunity costs of the products are constant
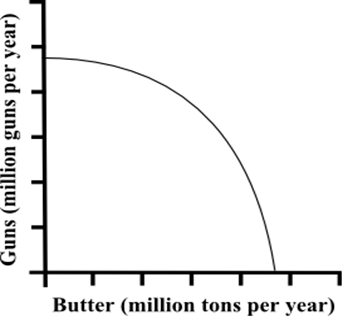
In a curved line PPC graph the opportunity costs of the products are increasing
Money
Money is anything that is generally accepted as a means of payment
Near money: non-cash assets that can be quickly turned into cash
Characteristics of money
- Acceptability
- Portability
- Durable
- Stability of supply and value
Classification of goods and services
Private goods: Consumed by some and it is not available for everyone
Public goods: It is non excludable and non rival and they are available for everyone
Quasi-public goods: A quasi-public good is a near-public good. It has some of the characteristics of a public good
Merit and demerit goods
Merit goods: Products that have positive side effects when consumed
Demerit goods: Products that have adverse side effects when consumed
