
Space Physics
Earth is a planet that rotates on its axis (tilted), once is 24 hours. This explains apparent daily motion of sun and the periodic cycle of day and night.
Earth orbits the sun once in 365 days and this explains the periodic nature of seasons.
Takes one month for moon to orbit earth and this explains periodic nature of moons cyclic phases.
Orbital speeds:
v = 2π r T where r is the average radius of the orbit and T is the orbital period
SOLAR SYSTEM:
The Solar System consists of:
- The Sun
- Eight planets
- Natural and artificial satellites
- Dwarf planets
- Asteroids and comets
ALL PLANETS have a gravitational field around them that can pull in surrounding objects (clear the neighbourhood) EXCEPT dwarf planets as their gravitational field is relatively weak.
Asteroids and comets also orbit the sun
An asteroid is a small rocky object which orbits the Sun
The asteroid belt lies between Mars and Jupiter
Comets are made of dust and ice and orbit the Sun in a different orbit to those of planets
The ice melts when the comet approaches the Sun and forms the comet’s tail
THE ACCRETION MODEL:
An interstellar disc cloud (nebula) of dust and gas is created
These clouds include many elements created during final stage of the life cycle of a star
Gravity collapses the matter in the nebula in on itself causing it to spin around the sun
INTERNAL Gravitational attraction between small particles causes them to merge and grow to form planets.
A ROTATING ACCRETION DISC is formed when planets emerge
Planetary trends:
The Sun is extremely hot and so when planets form near the sun the temperature is too high for Hydrogen, Helium, water and Methane to exist in a solid state.
Inner planets are made of elements with high melting points like iron
Inner planets are small, solid and rocky
Cooler outer planets allowed lighter molecules to be in a solid state. So they can grow large and are made of even hydrogen. They are LARGE, GASEOUS AND COLD
Elliptical orbits:
Sun is NOT THE CENTRE of an elliptical orbit except when the orbit is approximately circular
GRAVITATIONAL FIELD STRENGTH:
STRENGTH OF THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD AROUND A PLANET DECREASES AS THE DISTANCE FROM THE PLANET INCREASES
The Sun contains most of the mass in the solar system which is why planets orbit the sun
The Force that keeps a planet in orbit around the sun is the gravitational attraction of the sun
Gravitational field Strength decreases the further away a planet is from sun, leading to weaker centripetal force which gives a lower orbital speed
ELLIPTICAL ORBITS AND CONSERVATION OF ENERGY:
Radius changes if comets orbital speed changes
As a comet approaches sun, the radius of orbit decreases and the orbital speed increases
Throughout the orbit, gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy change. As the comet approaches the Sun it loses gravitational potential energy and gains kinetic energy and speeds up. The comet is then FLUNG back into space after passing around the sun. As the comet moves away from the sun, it gains gravitational potential energy and loses kinetic energy. Energy is conserved as the energy of the comet approaching the sun is equal in magnitude to the energy of the comet moving away from the sun. The comet slows down and falls back towards the sun to repeat its orbit.
STARS:
Galaxies are made of billions of stars and the sun is a star in the milky way galaxy. Stars that make up a galaxy are much farther from the earth that the sun is from the earth.
Milky way is one of the billions of galaxies in the universe and the diameter of the milky way is 100 000 light years.
Most of the mass of the solar system is concentrated in the Sun.
The Sun is medium sized star made of hydrogen and helium. It radiates most of its energy in the infrared, visible and UV regions of the Electromagnetic spectrum.
Colour emitted by star depends on how hot they are.
A RED STAR IS COOLEST AND A BLUE STAR IS THE HOTTEST
A Light year is the distance travelled by light through space in one year
one light year= 9.5x 10^15m
LIFE CYCLE OF STARS:
a star is formed from interstellar clouds of gas and dust that contain hydrogen
a protostar is an interstellar cloud collapsing and increasing in temperature as a result of its internal gravitational attraction
a protostar becomes a stable star when the inward force of gravitational attraction is balanced by an outward force due to the high temperature in the centre of the star
all stars eventually run out of hydrogen as fuel for the nuclear reaction
most stars expand to form red giants and more massive stars expand to form red supergiants when most of the hydrogen in the centre of the star has been converted to helium
a red giant from a less massive star forms a planetary nebula with a white dwarf star at its centre
a red supergiant explodes as a supernova, forming a nebula containing hydrogen and new heavier elements, leaving behind a neutron star or a black hole at its centre
the nebula from a supernova may form new stars with orbiting planets
BIG BANG THEORY, REDSHIFT AND CMBR:
EVIDENCE FROM BIG BANG- galactic red shift, cosmic microwave background radiation (cmbr)
REDSHIFT is the increase in the observed wavelength of electromagnetic radiation emitted from receding stars and galaxies.
Light spectra emitted from distant galaxies appear redshifted compared to earth emitted light
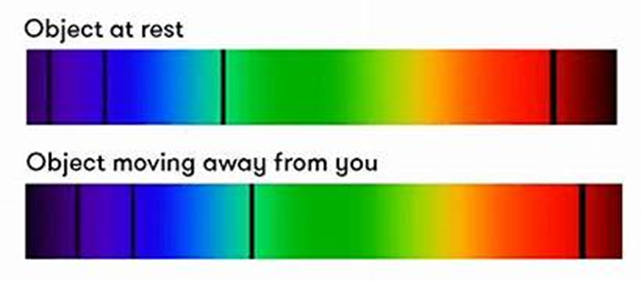
Galaxies are hence moving away from us and this means universe is expanding. Galactic redshift therefore supports the BIG BANG THEORY.
The Further away the galaxy is from earth, the faster it moves away from earth.
CMBR:
Cosmic microwave background radiation is an electromagnetic radiation formed in the early stages of the universes birth. It is extremely uniform and is observed in ALL points in space.
Bodies in the initial stages of the universes birth were extremely hot and thermal radiation was emitted. This radiation was in the gamma region of the spectrum, but the waves were slowly redshifted and the wavelengths were slowly increased to the microwave region of the spectrum.
THE Speed at which a galaxy is moving away from earth can be found by change in wavelength of a galaxy’s starlight due to redshift
THE Distance of a far galaxy can be determined using brightness of a supernova in that galaxy
Hubble:
Hubble’s law: recessional velocity of a galaxy is proportional to its distance from Earth
EQUATION:
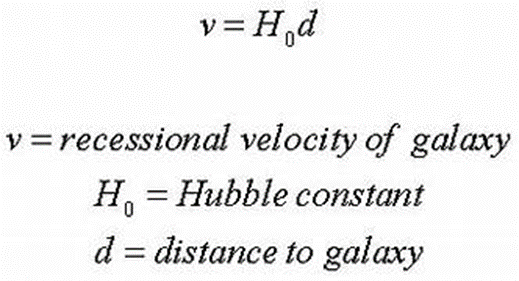
Hubble constant: ratio of the speed at which galaxy is moving away from the earth to its distance from the earth. Accepted value of the hubbles constant= 2.2x 10^-18 per second
The INVERSE OF THE HUBBLES CONSTANT IS AN ESTIMATE OF THE AGE OF THE UNIVERSE and the represents the fact that ALL MATTER in the universe was present at a single point.
1/H0 = d/v
